Distributed web3 cloud for running apps
Build and deploy scalable applications on Flux, a global, decentralized cloud computing network, enabling flexible, censorship-resistant development.
Control your data with decentralized cloud computing

Decentralized cloud computing distributes computing resources like RAM, storage, GPUs, and CPUs across a peer-to-peer (P2P) network of devices owned and operated by individual hardware providers.
Flux is powered by thousands of globally distributed, user-operated nodes. Leveraging geographically distributed individual hardware providers for computing resources, rather than a single organization, creates a broader attack surface, making Flux inherently secure.
Decentralized cloud networks ensure fast data transmission, and their distributed hardware eliminates single points of failure while creating resilience and redundancy. Because of so many individuals providing computing resources, even if one part of the cloud goes down, the rest of the network can still function.
Next generation of the web: Decentralized, secure, and powered by Flux.

Made for Developers
Distributed Hardware
Independently owned and operated hardware, globally distributed for local and low-latency deployments. A network of providers powers your apps, not one central company.
Interoperable
Flux is code-agnostic, with Docker container deployments and custom integrations via FluxAPI plugins. Our system works universally across different programming languages.
Secure Infrastructure
Flux prioritizes application security. Docker Hub, IPFS, 24/7 monitoring, and pre-allocated disk space secured by ArcaneOS help provide additional layers of safety.
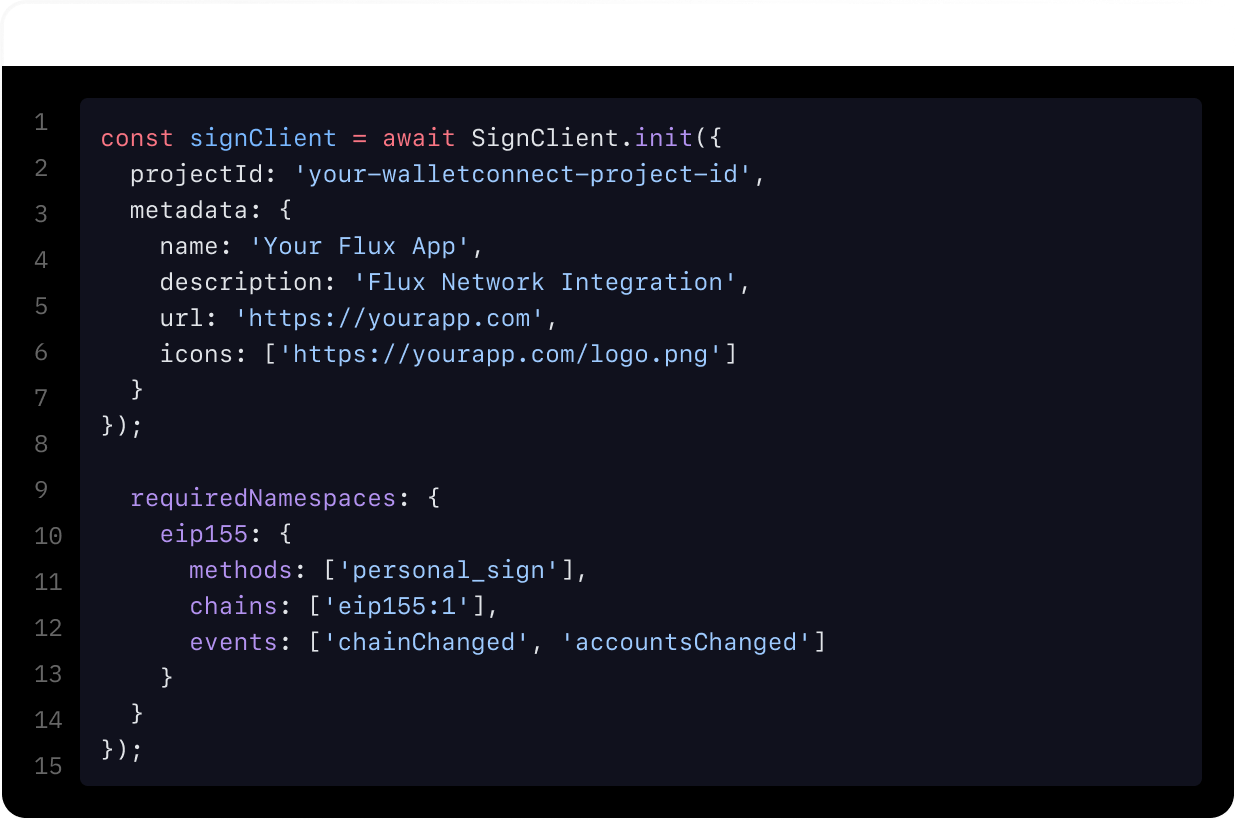
Extensive Docs
Flux streamlines app development through comprehensive documentation. We want to make it seamless for new users unfamiliar with decentralized cloud technology.
With in-depth set up guides across every product offering, Flux Docs is a resource that facilitates a smooth developer experience from providing data to deploying an app.

Unlimited Scalability
Flux being powered by a global network of distributed hardware means limitless scalability as compute is being sourced from so many independent providers, rather than a single provider with centralized datacenters.
Independent hardware providers join the Flux network and supply compute by harnessing the underutilized bandwidth of their personal devices, enabling censorship-free app development for users.
Flux delivers a decentralized cloud solution where the supply of computing resources is distributed across many independent hardware providers. Applications receive dedicated compute from a diverse range of enterprise-grade GPUs at a fraction of the cost of traditional public cloud providers.

Total Nodes worldwide
CPU Cores
Ram
SSD Disk
Flux Foundation
Community-governed and wholly transparent, the Flux Foundation serves as a sustainable growth engine for the Flux decentralized cloud network.
The Foundation receives a fixed portion of block rewards, acting as a consistent revenue stream to fund network growth through yield-generating infrastructure.

Elevate with cutting-edge tech fully managed by our team
Launch and deploy apps with our help. Experience fully-managed service processes with 24/7 developer support from InFlux Technologies. Leverage our innovative decentralized cloud network to transform your business into a scalable enterprise, driving growth through user participation.